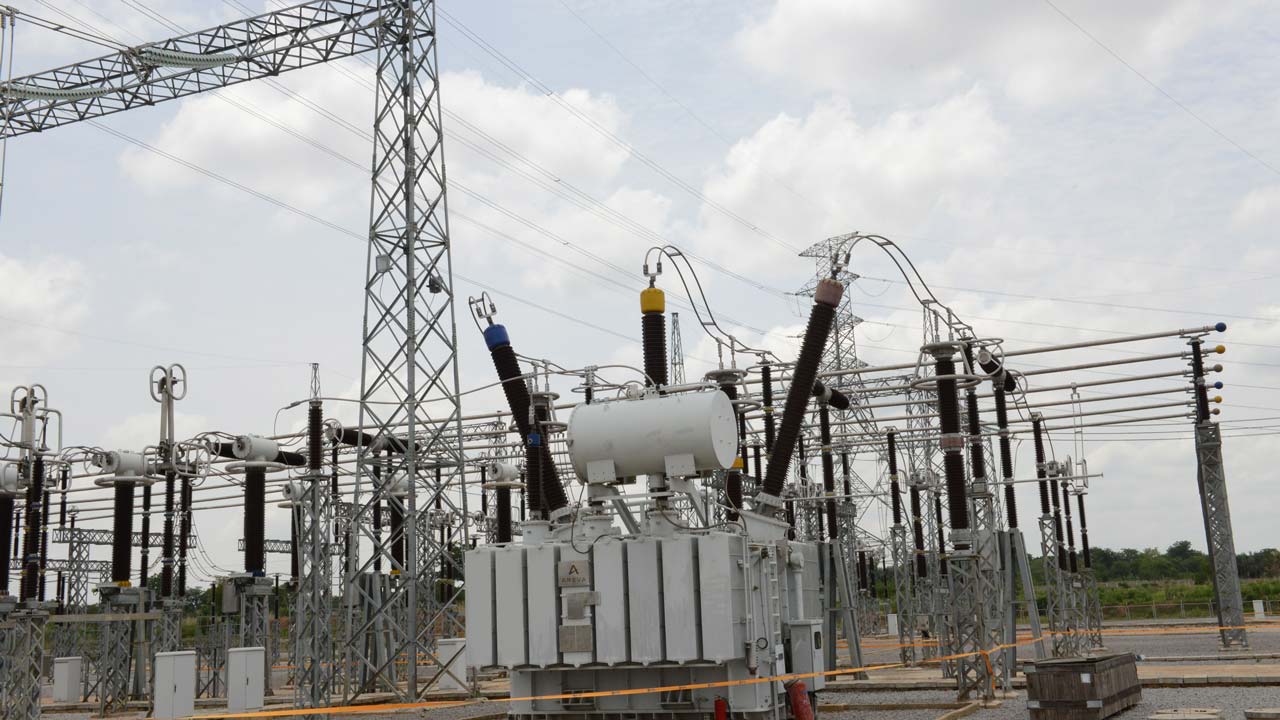
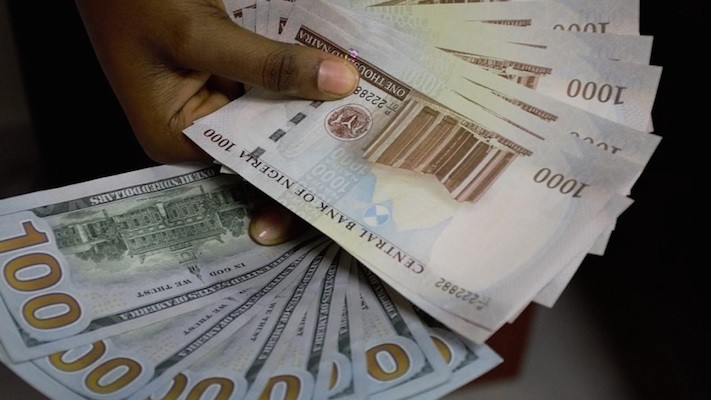
Nigeria is bracing itself for a challenging period ahead as the electricity tariff is set to increase by more than 40%, potentially putting an end to all energy subsidies in the country.
With a monthly subsidy of approximately N50 billion still present in the electricity sector due to revenue shortfalls, the tariff hike scheduled for July 1st will be another significant test for President Bola Ahmed Tinubu’s administration’s market reform efforts.
The administration has already eliminated subsidies on Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) and implemented a floating exchange rate for the naira, both of which have complicated the price-setting process of the Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission’s (NERC) 2022 Multi-Year Tariff Order (MYTO).
Despite signing contracts with NERC to ensure a supply of at least 5,000 megawatts per year, the power sector players have been unable to meet this target.
In 2015, the average tariff for distribution companies (DisCos) and different customer classes was N25 per kilowatt. However, in the 2020 MYTO, the average tariff rose to N60 per kilowatt, and in the 2022 MYTO, it further increased to N64 per kilowatt across customer classes.
Foreign exchange rates and inflation have played a crucial role in determining the tariffs. The exchange rate used in 2015 was N198.97/$, which increased to N383.80/$ in 2020, and N441.78/$ in 2022. Inflation rates used were 8.3% in 2015, 12% in 2020, and 16.97% in 2022.
Currently, the inflation rate stands at 22.41%, with projections indicating it could reach 30% by the end of June due to the floating of the naira and the removal of PMS subsidies.
Besides inflation, other factors such as the metering gap of over seven million, gas prices, losses, and actual generation capacity also contribute to the determination of tariffs.
While NERC’s projected tariff for July 2023 aimed to remove subsidies and increase the previously frozen tariff bands D and E, the prevailing floating of the naira and rising inflation are expected to push the new average tariff to approximately N88 per kilowatt, allowing the sector to recover its costs.
Stakeholders have expressed concerns over the unavoidable tariff increase and its potential impact on households and small businesses. Energy costs alone are expected to rise by over 70%, placing further strain on purchasing power amidst high unemployment and poverty rates, which form significant challenges for the economy.
As of now, the available electricity on the grid stands at 3,057.7 megawatts from 17 power plants. Over the past four months, the average load intake of all DisCos has been around 3,000 megawatts, falling significantly short of the 100% remittance orders they are required to meet.
The unreliability of the grid and subsequent financial losses have raised concerns among stakeholders about the future of the Nigerian Electricity Supply Market. Consumer apathy towards the system and the increasing reliance on alternative energy sources are compounding the sector’s challenges.
Energy expert, Prof Wunmi Iledare, expressed concerns about the restructuring of the forex market and its potential devaluation of the naira. He emphasized the importance of supporting the government’s efforts to decouple the economy from forex instability, even if it means accepting higher electricity tariffs and petroleum product prices.

 Education4 weeks ago
Education4 weeks ago


 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks ago


 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks ago


 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago


 Investment4 weeks ago
Investment4 weeks ago
 Investment3 weeks ago
Investment3 weeks ago
 Telecommunications4 weeks ago
Telecommunications4 weeks ago

 Banking Sector3 weeks ago
Banking Sector3 weeks ago

















