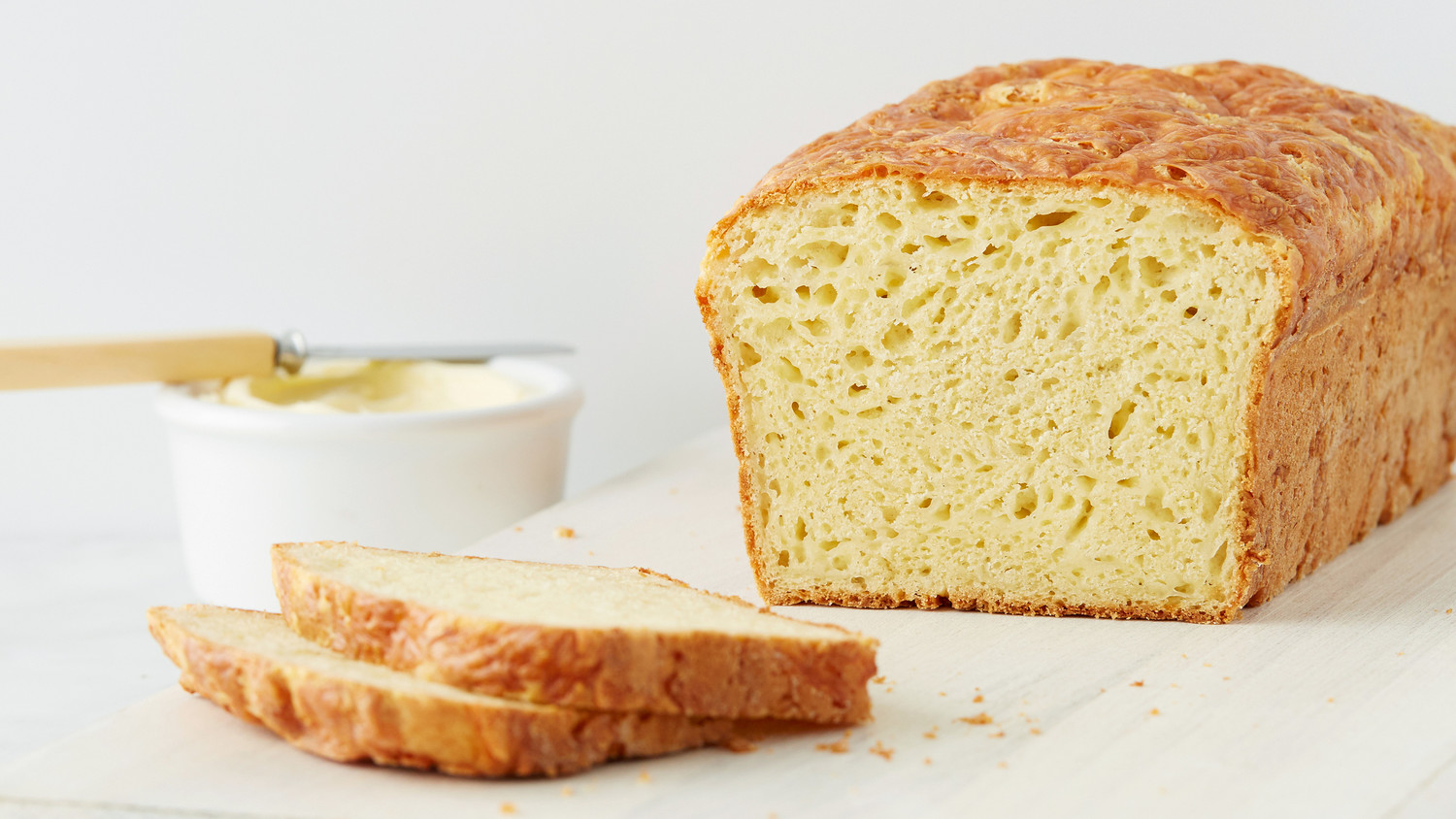
Post Covid-19 Economy in Nigeria Sees Scarcity And Price hike in Bread Production
Residents of Abuja and Lagos are lamenting the increased scarcity in bread and a hike in its price as bakers went on strike to protest the hike in price of flour and other ingredients.
“I have asked around for bread but I can’t find any, and this is strange,” said Amos Idoko, a resident of Utako area in Abuja.
The strike affected roadside kiosk operations and families who rely on bread for a breakfast staple with many running out of bread last weekend across some communities surveyed in the FCT, Nasarawa and Niger state.
Some of the bakers said the strike started Friday and may end today, but there will be a hike in the price of bread.
A leader of the bakers group in the FCT and an official of Zuma Bread in Abuja, Abdullahi Muhammed, said the strike action was to protest the hike of flour and other ingredients for bread making.
Daily Trust reported exclusively recently that foreign-dominated flour millers have increased the price of flour for more than three times between March and August 2020, even with the COVID-19 pandemic.
“For instance, a bag of wheat flour sold between N10,000 and N12,000 last year now sells for N14,000,” he said
“Bag of sugar sold for about N11,000 last year now sells at N18,000. A 25-litre cooking oil previously N8,000 is now N15,000,” he said.
A dealer in wheat flour and baking ingredients in Kubwa – Abuja, Shehu Lawan, said dealers now rely on the parallel market to source for forex instead of the Central bank of Nigeria (CBN), making it difficult for them to maintain previous prices.
Lawan also said other issues that affect cost in bakery commodities, include government tax increment, cost of transport, among others.
In Lagos, Mr Ajao Ismail, who works at Royal Bite bakery in Palm Avenue of Mushin, said there was an earlier scarcity of bread in Lagos but that most bakers have resumed operations as of Sunday evening but with the bread price increasing.
“The market is dull at the moment because we have lots of bread that we have not sold. When there was scarcity, the demand was higher than the supply, now that most of the bakers are no longer on strike, there is more bread. People are reacting to the price.”
Ajao explained that the price of bread can return to how it was pre-COVID provided the government intervenes.
“If the government can work towards ensuring the price of flour, sugar, milk and butter is reduced to what it was in January 2020, we promise to reverse the price of bread to what it was.
“Bread now sold for N300/350 will return to N250 and the one sold for N500 will return to N400,” she noted.
The bakers had shut down for a number of days last week in Lagos. Premium Bread makers Association of Nigeria (PBAN) and Association of Master Bakers and Caterers Association of Nigeria (AMBAN) in briefing said the prices of ingredients
The spokesperson of PBAN, Emmanuel Onuoha, confirmed the scarcity. “If we don’t do this, people will think it is their right to buy cheap bread,” he said, adding that bakers now run at a loss even as most of them could no longer meet their loan repayment obligations.
It was also learnt that other states might also embark on the temporary cessation of production in response to the high cost of baking ingredients comprising flour, sugar, margarine, among others.

 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks ago
 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Investment3 weeks ago
Investment3 weeks ago
 Banking Sector3 weeks ago
Banking Sector3 weeks ago
 Banking Sector3 weeks ago
Banking Sector3 weeks ago
 Appointments3 weeks ago
Appointments3 weeks ago
 Investment3 weeks ago
Investment3 weeks ago