- US Fed Cuts Interest Rate by 50 Basis Points
The Federal Reserve on Tuesday reduced Interest rate by 50 basis points amid falling stocks as Coronavirus ravages both local and global economies.
The uncertainty surrounding the world economy due to the global health crisis weighed on stocks of American companies and rendered Wall Street volatile despite progressive growth recorded in recent months.
Jerome Powell, Chairman, Federal Reserve, however, said the risk to the American economy is a material risk, therefore, in order to ensure employment growth and price stability, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) lowered the benchmark rate by half percentage point to support economic activities.
“The coronavirus poses evolving risks to economic activity,” the Fed said in a statement. “In light of these risks and in support of achieving its maximum employment and price stability goals, the Federal Open Market Committee decided today to lower the target range for the federal funds rate.”
In a news conference after the decision, the Chairman said policymakers took the decision after noticing coronavirus was having a material effect on the economy.
“The magnitude and persistence of the overall effect on the U.S. economy remain highly uncertain and the situation remains a fluid one,” he told reporters. “Against this background, the committee judged that the risks to the U.S. outlook have changed materially. In response, we have eased the stance of monetary policy to provide some more support to the economy.”
Still, President Trump felt the Federal Reserve could do more, saying the fed needs to increase stimulus and cut even more to support American companies, especially with the capital flight to haven assets rising. The US needs to be on even playing field with other nations struggling with coronavirus and growth.
However, market experts doubt the cut would have a meaningful impact given the size of the crisis. “Until an effective solution to curb the fast-spreading virus or cure is found, the risk to the global economy remained high and even at a zero interest rate, Federal Reserve may not be able to contain falling growth,” stated Temitayo Sikiru, a business analyst with Investors King Ltd.
“What it does more than anything else is it improves sentiment and buys time for fiscal authorities to figure out the response to the economic consequences of the virus,” said Solita Marcelli, deputy chief investment officer for the Americas at UBS Global Wealth Management. “They need the support of fiscal measures. I don’t think alone on its own the [rate cut] is going to be able to uplift the negative economic impact.”
In fact, Wall Street is predicting zero interest rates by the end of the year as traders and investors doubt the current action would completely address growth issues in the world’s largest economy and prevent job loss.
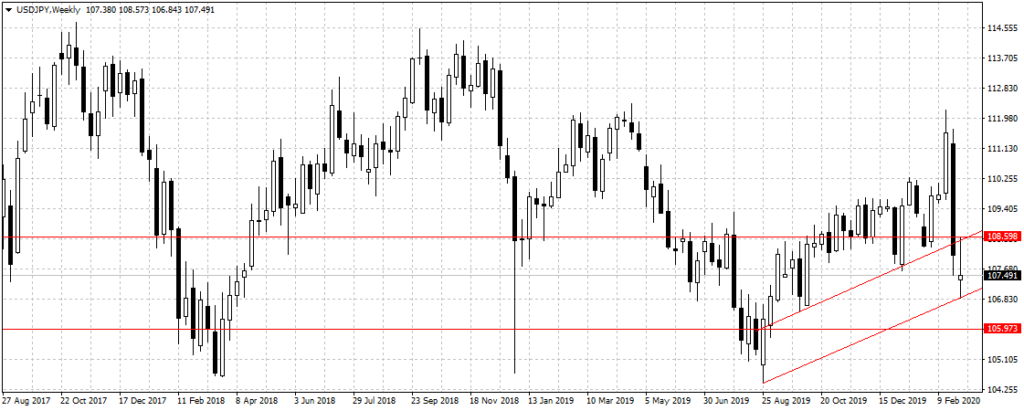
The US dollar was unchanged against the Japanese Yen immediately the rate was lowered, however, plunged to five months low after traders digested the content of the report amid doubts the action would be enough to sustain the greenback above the current level as shown below.
 “The committee obviously decided not to wait for things to deteriorate — I think they know as we all should that the headlines over the next few days are likely to be alarming as they pertain to the spread of the virus,” said Eric Winograd, senior economist at AllianceBernstein. “The Fed obviously cannot address the virus itself by cutting rates, but they can hope to short circuit the potential for a negative response in financial markets that could make the economic impact of the virus even worse.”
“The committee obviously decided not to wait for things to deteriorate — I think they know as we all should that the headlines over the next few days are likely to be alarming as they pertain to the spread of the virus,” said Eric Winograd, senior economist at AllianceBernstein. “The Fed obviously cannot address the virus itself by cutting rates, but they can hope to short circuit the potential for a negative response in financial markets that could make the economic impact of the virus even worse.”

 Forex3 weeks ago
Forex3 weeks ago
 Naira3 weeks ago
Naira3 weeks ago
 Billionaire Watch2 weeks ago
Billionaire Watch2 weeks ago


 Naira3 weeks ago
Naira3 weeks ago




 Naira2 weeks ago
Naira2 weeks ago




 Naira1 week ago
Naira1 week ago




 Naira4 weeks ago
Naira4 weeks ago
 Banking Sector4 weeks ago
Banking Sector4 weeks ago

























