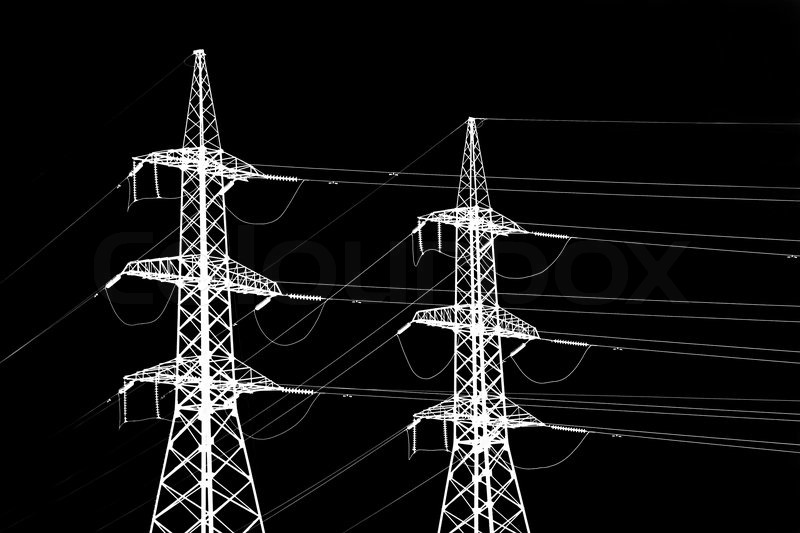
Power GE safely completed service interventions on three GE 9E gas turbines at the Niger Delta Power Holding Company (NDPHC) power plants in Calabar and Sapele, Nigeria; With compressive safety measures due to COVID-19 in place, GE and NDPHC quickly ensured both employee safety and on-time project execution; Outages were executed on time and the restored power will enable NDPHC to provide the equivalent electricity needed to power up to 2 million Nigerian homes.
GE (NYSE: GE) today announced the successful rehabilitation of three 9E.03 gas turbines, at three Niger Delta Power Holding Company’s (NDPHC) Power Plants in Calabar and Sapele, Nigeria. These operations reduced the risk of unplanned downtime of its power generation equipment, enabling the plants to reliably secure and restore the supply of up to 360 megawatts (MW) of electricity to the national grid, the equivalent electricity needed to power approximately two million Nigerian homes. Despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, GE and NDPHC worked together to swiftly implement safety procedures to ensure a safe and on-time execution.
“Being Nigeria’s largest electricity generating company, with a total installed capacity of 4.0 gigawatts (GW), representing about 35% of Nigeria’s generating capacity, we are committed to strengthening Nigeria’s power sector, despite the unexpected logistical challenges of the COVID-19 outbreak,” said Chiedu Ugbo, Managing Director, NDPHC. “GE’s efficiency to mobilize local teams on-site with the required technical skills and expertise, as well as GE’s global supply chain scale was crucial to ensure the timely and safe completion of the outages at the sites and help us achieve our goal.”
The outages involved stage three bucket changeouts on three 9E gas turbines as well as additional combustion inspections. Engineers from GE and FieldCore, the field services execution company owned by GE, worked together and in close collaboration with NDPHC to implement additional safety measures and reduce the risk of exposure to COVID-19, including frequent disinfections at the site, physical distancing, standard passive and active temperature screenings for personnel, and the use of personal protective equipment such as masks and gloves.
“We are committed to supporting power plant operators like NDPHC to be able to provide reliable power with exceptional support and services from GE throughout these uncertain times, while ensuring and maintaining the health and safety of our employees and suppliers.” said Elisee Sezan, CEO for GE’s Gas Power business in Sub-Saharan Africa. “The successful rehabilitation of the power generations assets at Calabar and Sapele plants will help increase the 9E gas turbines’ efficiency, while lowering emissions and providing essential power for industrialization, healthcare facilities, homes, schools and businesses.”
This year, GE’s 9E gas turbine fleet celebrates 40 years of operations globally. The 9E is a robust, proven platform that delivers high availability, reliability, and durability while lowering the overall cost-per-kilowatt. It has a large installed base of over 650 units in the world located primarily in Asia, China, Europe, Africa and the Middle East.
GE has been collaborating with energy stakeholders to deploy innovative technologies tailored to respond to the needs in the region since the 1950s with reliable baseload and flexible emergency power. In 2018, the company celebrated its 100th power plant in Sub-Saharan Africa and today, up to 17 GW of gas power generation on the grid runs on GE gas turbines. GE delivers across the entire energy ecosystem from generation to transmission and distribution and throughout Nigeria, GE-built technologies are supported by local service and maintenance teams from the company to ensure access to reliable and sustainable energy.



 News3 weeks ago
News3 weeks ago


 Business3 weeks ago
Business3 weeks ago


 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Investment3 weeks ago
Investment3 weeks ago

 Banking Sector3 weeks ago
Banking Sector3 weeks ago
 Banking Sector3 weeks ago
Banking Sector3 weeks ago
 Appointments3 weeks ago
Appointments3 weeks ago
 Investment3 weeks ago
Investment3 weeks ago

















